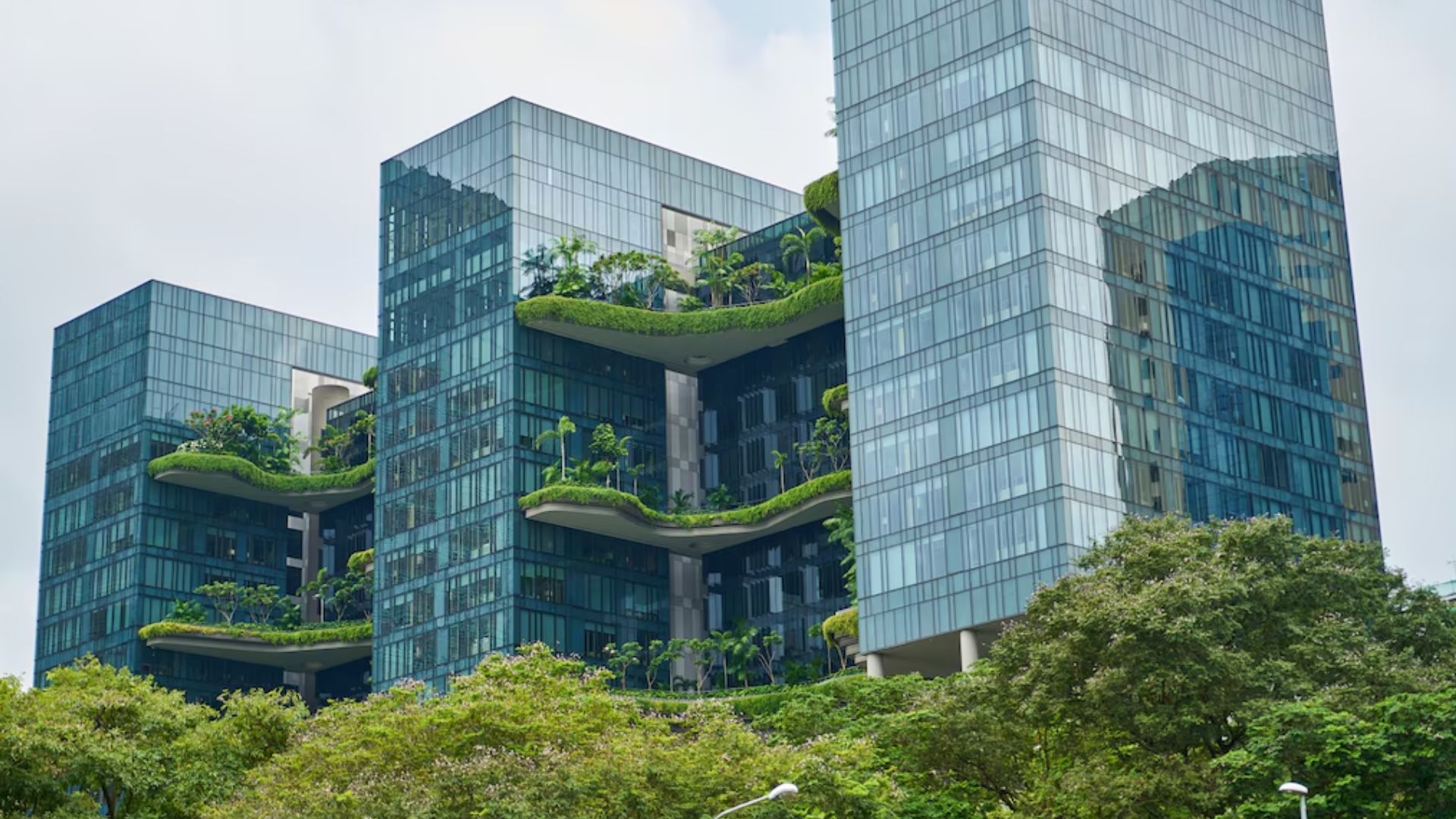
Businesses in India are realizing more and more how important it is to include ecologically friendly practices in their operations as sustainability becomes a global necessity. The panorama of sustainable business practices in India will be examined in this essay, along with the advantages, difficulties, and tactics for organizations looking to follow the road of environmental stewardship.
1. Sustainable Business Practices Are Important:
- Environmental Impact: Companies have a major influence on environmental issues, and reducing adverse effects on the environment requires the adoption of sustainable practices.
- Consumer Preferences: Sustainability is a crucial component of brand reputation and customer loyalty since modern consumers are more likely to support companies that practice environmental responsibility.
2. Important Sustainable Business Methods:
- Renewable Energy Usage: To lessen reliance on fossil fuels, switch to renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
- Resource Efficiency: Putting policies in place to maximize resource utilization, cut waste, and advance recycling and the ideas of the circular economy.
- Green Supply Chain: Establishing a sustainable and ethical supply chain by working with suppliers who follow these principles.
3. India’s Regulatory Environment:
- Environmental rules: Being aware of and abiding by India’s environmental rules and regulations, which regulate things like pollution control, waste management, and emissions.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Adhering to the Companies Act’s CSR rules, which incentivize companies to support environmental and social concerns.
4. Advantages of Eco-Friendly Behavior:
- Cost Savings: Over time, implementing energy-efficient technologies and cutting waste can result in significant cost savings.
- Improved Brand Image: By drawing in eco-aware customers and investors, a company’s dedication to sustainability improves its brand image.
- Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Following environmental laws lowers the possibility of legal problems and fines from the government.
5. Difficulties with Sustainability Implementation:
- Initial Investment: Some businesses may find the upfront expenses of adopting sustainable practices and technologies to be a deterrent.
- Alter Management: Organizational culture and staff behavior may need to alter in order to transition to sustainable practices.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Managing multiple suppliers can make it difficult to ensure sustainability throughout the supply chain.
6. Technology and Innovation for Sustainability:
- Research and Development: Funding the creation of innovative and sustainable technologies.
Using digital tools to operate remotely reduces the demand for physical infrastructure and the environmental effects that come with it.
7. Transparency and Corporate Reporting:
- Environmental Reporting: Putting in place clear reporting procedures to reveal environmental performance, objectives, and accomplishments.
- Certifications: Seeking and acquiring environmental management system certifications, such as ISO 14001.
8. Stakeholder Engagement:
- Employee Involvement: Promoting a sense of responsibility among staff members by motivating and involving them in sustainability projects.
- Community Outreach: Talking to stakeholders and local communities to address their issues and support sustainable development.
9. Practices of the Circular Economy:
- Product Life Extension: Increasing the lifespan of items by designing them to be durable and repairable.
- Recycling methods: Putting in place efficient methods for recycling goods and packaging.
10. Industry Initiatives and Collaboration:
- Industry Alliances: Working together with competitors and colleagues in the industry to exchange best practices and advance group sustainability projects.
- Government Partnerships: Taking part in government campaigns and projects that support environmentally friendly corporate operations.
11. Adaptability and Ongoing Improvement:
- Regular Audits: Performing routine audits to evaluate how operations affect the environment and pinpoint areas in need of change.
- Adaptability: Keeping up with changing best practices and trends in sustainability while remaining adaptable.
12. Integration with Business Strategy:
- Strategic Alignment: Integrating sustainability goals seamlessly into the overall business strategy for long-term success.
- Board and Leadership Involvement: Ensuring that sustainability is a priority at the board and leadership levels.
Conclusion:
In India, using sustainable business practices is not just a duty but also a chance for companies to prosper in a world that is changing. Businesses can improve their competitiveness, brand image, and ability to withstand changing social expectations by adopting environmentally conscious practices. They can also help create a healthier planet.
Read More Articles: Click Here